

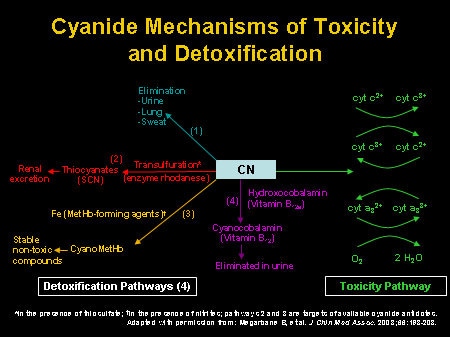

Lastly, a new approach to cyanide antagonism has been initiated which involves the erythrocyte encapsulation of thiosulphate and sulphurtransferase as an antidote and prophylaxis against cyanide. The roles and implications of sodium thiosulphate and non-rhodanese substrates in the detoxification mechanism are compared. This suggests that methaemoglobin formation plays only a small part, if any, in the therapeutic antagonism of the lethal effects of cyanide. Sodium Thiosulfate Injection is indicated for sequential use with sodium nitrite for the treatment of acute cyanide poisoning that is judged to be serious or. In the nitrite-thiosulphate antidotal combination, the proposal is made that the predominate antidotal action of nitrite is a vasogenic action, rather than methaemoglobin formation, because when methaemoglobin formation is inhibited by methylene blue the protective action of sodium nitrite persists. Theoretically, increased oxygen should serve no useful purpose, as it is the tissue utilization of oxygen which is inhibited. Oxygen with nitrite-thiosulphate antagonizes the lethal effects of cyanide. Questions have been raised with regard to these classical mechanisms. One mechanism of cyanide antagonism is by sequestering cyanide with methaemoglobin to form cyanmethaemoglobin and another mechanism is detoxifying with a sulphur donor to thiocyanate. The mechanism of toxicity occurs because cyanide stops the cells of the body from being able to use oxygen, which all cells need to survive. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for cyanocobalamin as a valuable agent in managing vitamin B12. The name cyanocobalamin derives from the cyanide group attached to the molecule. Chemically it belongs to a class called 'corrinoids,' and it is a crystallizable cobalt complex. The mechanism of cyanide intoxication has been attributed to the inhibition of cytochrome oxidase, thereby decreasing the tissue utilization of oxygen. Cyanocobalamin is a medication used to manage and treat vitamin B12 deficiencies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
